Posts Tagged ‘Silver Coin’
The making of a true Masterpiece…
Each year Remembrance Sunday provides an opportunity for the nation to reflect on those brave men and women who gave their lives fighting for our freedom. But this year will be especially poignant. As we also commemorate the 80th Anniversary of one of the truly remarkable chapters in our nation’s history – the Battle of Britain.
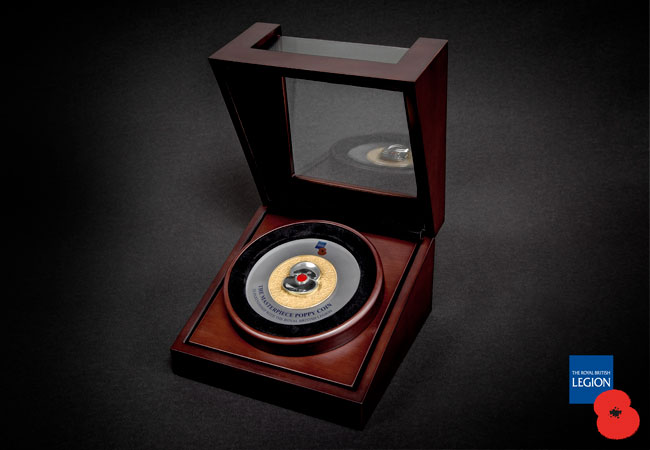
Introducing the official 2020 Remembrance Masterpiece Silver 5oz Poppy Coin
There is one coin that avid collectors await the release of – the “Masterpiece Poppy Coin”. The name says it all. Cutting edge minting techniques and materials, representing the pinnacle of craftsmanship. But let me explain what makes this year’s Masterpiece Poppy so special…
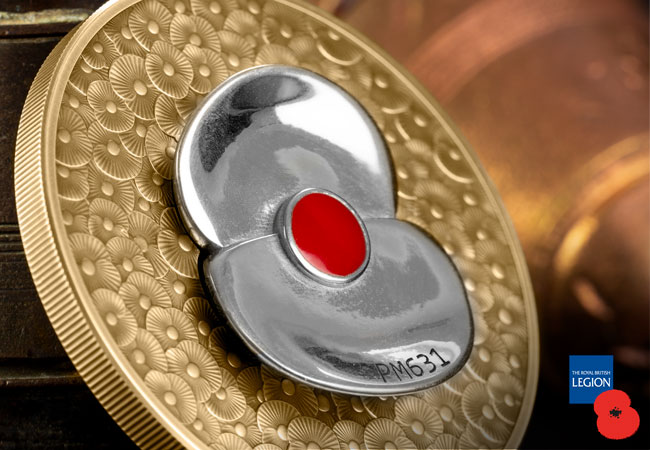
This year marks the 80th anniversary of the Battle of Britain. Take a look at the images and you’ll see that a single stylised Royal British Legion poppy, proudly sits on top of this coin. Multiple poppies have then been engraved into the surface of the coin, resulting in an exceptional 3 dimensional effect.
But the incredibly rare facet of this year’s poppy coin is that it’s been crafted from a genuine piece of Spitfire.
Expertly crafted from a Spitfire with a remarkable story to tell
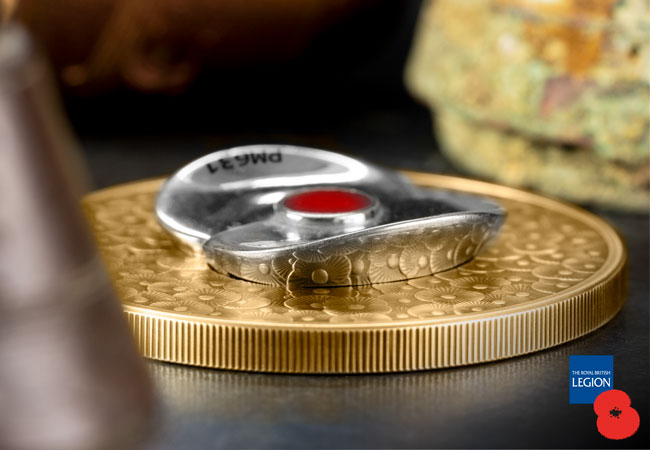
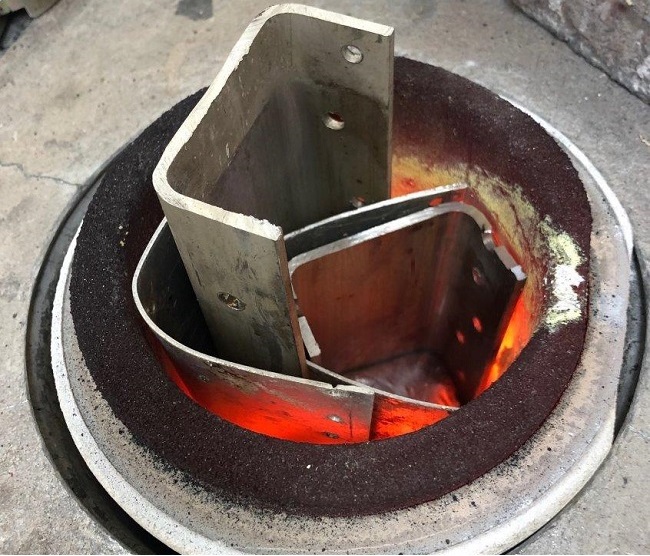
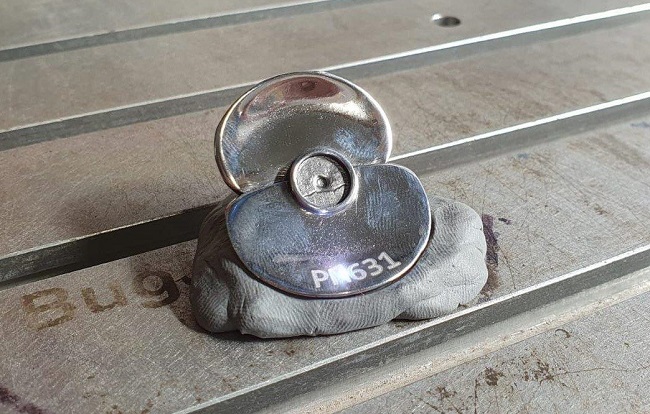
Incredibly, this year, the silver poppy that adorns the reverse of each of these coins has been made from a piece of Spitfire PM631 – ensuring each coin is uniquely different and features a piece of tangible aerial history.
Originally built in late 1945, the Spitfire PM631 saw service with the Battle of Britain memorial flight for nearly FIFTY years between 1957 and 2006. You may also remember that it had a starring role in a famous WWII Movie – Battle of Britain, made in 1969.

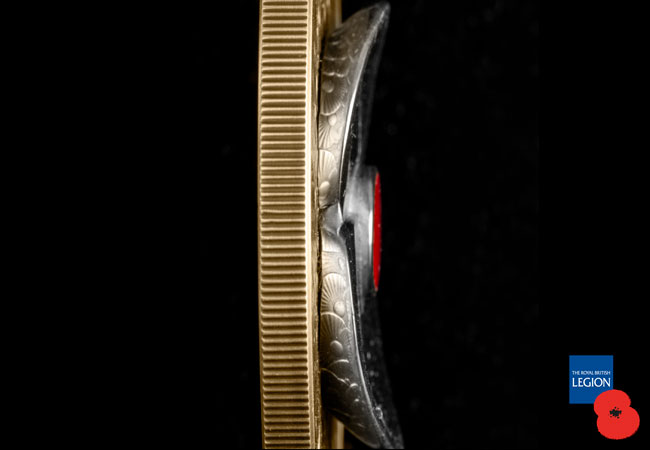
Once the Spitfire piece has been melted down and poured into a shaped mould, it is cooled and cleaned to create the high-relief poppy. After this, it is laser engraved with the official Spitfire plane from which the metal was taken – PM631. Check out the images below to see the process the Spitfire metal goes through to come a Masterpiece poppy…
But even then, it is important to remember, this is NOT a cast piece. The surface of the coin has actually been struck in sterling silver and has then expertly plated in 24ct gold. The finish is a stunning matte appearance achieved using a technique called ‘Sandblasting’. This means it has all of the detail that you expect from a commemorative coin but allows you to touch the coin and hold a genuine, iconic piece of history in the palm of your hand.
As I am sure you can appreciate, given all of the individual elements that have to be carefully curated for each individual coin, the edition limit as a consequence is incredibly low. In fact, only 300 of these coins have been produced, with number one fittingly being donated to The Royal British Legion themselves. Which means only 299 coins remain for collectors.
We do not expect these coins to be around for long. And remember, for each coin sold a donation will go straight to The Royal British Legion in support of all their work.
Available now – with a donation to The Royal British Legion
The 2020 Masterpiece 5oz Silver Proof Poppy Coin is available to own right now from The Westminster Collection, although they are expected to sell out quickly.
To further support the work of The Royal British Legion, a donation of £59.50 from the sale of each coin will go directly to the charity, helping them to continue to provide financial, social and life-long support to the Armed Forces community.
£1,100,000 Milestone
What’s more, since our partnership began and through the sales of commemorative Remembrance and Poppy-themed coins, collectors have helped raise an incredible £1.1 Million for The Royal British Legion!
This is an achievement that everyone is immensely proud of, and we are hugely thankful to collectors for helping raise such an amazing amount.
If you’d like to find out more about the fantastic work that The Royal British Legion do and why we are so proud of this milestone £1.1 Million that has been raised for the charity, then click here to read more…
EXPERT GUIDE: building a historic coin collection
One of the questions I get asked most, by my friends and others in the coin business, is: what is the best (and most affordable) way to build an enviable collection of historic coins?
There are so many fascinating coins in British history, it’s a question that is hard to answer. Where do you start!?
Which is why I’ve decided to put together an Expert Guide to building a collection of historic coins, by answering some of the questions I hear most often from collectors…
How far back can I go?
One of the questions collectors face when they first start collecting historic coins is: how far back can I go? Is a Victorian coin affordable, and did every monarch release coins?
As a general rule, coins tend to get more expensive the further back in time you go. Which is why owning a coin from our current monarch is the best place to start. You can then work your way back through other famous monarchs.

Most collectors can aim to collect coins from each monarch back to the 17th century. After the tumultuous leadership of Oliver Cromwell, Charles II reclaimed the throne and began a period of standardised coin issue. For most collectors it’s possible to collect coins back to this fascinating period in history without breaking the bank!
Which are the important monarchs?
A great coin collection should contain coins issued by famous monarchs, monarchs that changed the history of our nation and ones that revolutionised our coinage.
An obvious monarch is Queen Victoria – the monarch who built the largest Empire the world has ever seen and who oversaw some of the greatest changes our nation has ever experienced. And every collection should contain an important issue by our current monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, the longest reigning monarch in our nation’s history! And you can’t leave out George III, not only did he oversea a complete overhaul of our currency but he’s also our longest reigning King.
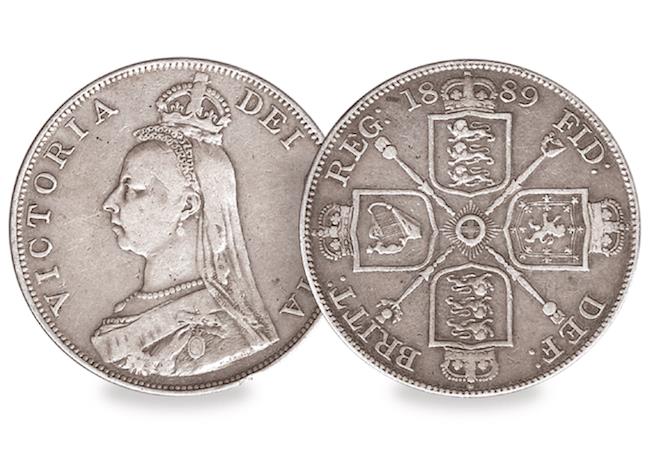

Those are just a few of the key monarchs, but once you start collecting you’ll find that each monarch has a fascinating story and a number of really interesting coin issues.
Base metal, Silver or Gold?
Gold has historically been seen as the pinnacle for collectors. But this famous metal comes with its difficulties. Gold coins were issued in much smaller numbers, and not every monarch released a standardised gold coin. Which means that to own a Gold coin from some monarchs is extremely difficult – for example George VI only issued a Sovereign for one year of his reign.

Base metal and Silver coins tend to be much more achievable for most collectors. Base metal coins (pennies, farthings and the like) tend to be less expensive, however because of their lower value the quality of coins can vary widely. Silver coins were issued by most monarchs, and because of their slightly higher value tend to be found in better grades.
How should I store my coins?
The wear and tear of an old coin is part of the appeal of collecting historic coins, but it’s important to protect your coins from any outside interference that could potentially discolour, wear or generally affect the condition of your coin.
I would recommend always storing your coins in capsules, and if possible in a tamperproof capsule that will guarantee the condition of your coin for generations to come. And as you build your collection, there’s nothing better than having a box with trays to keep your collection together for you to store and present.
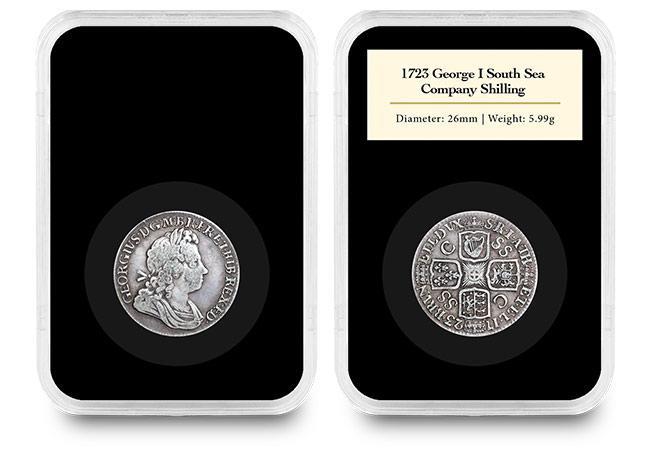

How much will it cost me?
For most collectors building a historic coin collection, one of the most confusing elements can be price. The prices for historic coins can vary widely – you might find an old Victorian penny at a car boot for less than £10 and then see what looks like the same coin selling for hundreds on an online auction site.
I’d always recommend purchasing carefully, preferably by making sure you either have an expert opinion or by ordering from a reputable retailer. By making sure you’re getting your coins from the right place, building a collection of Silver coins back to the 17th century is actually more affordable than many collectors realise – in fact most coins should cost between £100 and £500.
Lastly… have fun!
The most important part of collecting coins is having those coins in your hand and feeling the history your coin has carried with it over generations. So have some fun and get collecting!
If you would like to learn more about building your own historic coin collection, with some expert guidance, just fill out the form below. One of our team will be in contact with you soon:
Your message has been sent
How a £10,000 reward led to one of the greatest advancements in aviation
In the 1800’s, when aeroplanes were a mere twinkle in the eye of ambitious engineers, the idea of transatlantic flight came about with the advent of the hot air balloon. But one crash-landing, and one postponement due to the American Civil War meant this dream had to go back to the drawing board.
On the other side of the pond, in April of 1913 The Daily Mail newspaper offered a cash prize of £10,000 to “the aviator who shall first cross the Atlantic in an aeroplane in flight from any point in the United States of America, Canada or Newfoundland and any point in Great Britain or Ireland in 72 continuous hours”.
But it wasn’t until after the end of WWII that transatlantic flight by aircraft became truly viable, thanks to the significant advancements in aerial capabilities and technology.
Then the competition really heated up…
Nail-biting four-way competition
What came was a nail-biting four-way contest against the clock as well as each other. Four different ‘teams’ formed and went to work to try and prepare their chosen aircraft the fastest, for fear of being pipped to the post by another team making their attempt sooner. To make it a fair contest, each team had to ship their aircraft to Newfoundland for the take-off.
First to try was Australian pilot Harry Hawker and navigator Kenneth Mackenzie Grieve, piloting a Sopwith Atlantic – an experimental British long-range aircraft. In flight the aircraft suffered from engine failure and, when coupled with poor weather conditions, the decision was made to abort the mission.
The aircraft was abandoned in the Atlantic Ocean, 750 miles from Ireland, and the pair were rescued by a Danish steamer SS Mary. Due to the SS Mary not having any radio contact, the pair were presumed dead and King George V sent a telegram of condolence, but luckily this wasn’t the case as the pair arrived back on land nearly a week later.
The next attempt wasn’t nearly as exciting, as the aircraft never left the take-off zone. Frederick Raynham and C. W. F. Morgan made the attempt in a Martinsyde but crashed on take-off due to the heavy fuel load.
Then came the turn of aviator duo, John Alcock and Arthur Brown, who flew straight into the history books on June 15th 1919…
Flying in to the unknown across the Atlantic
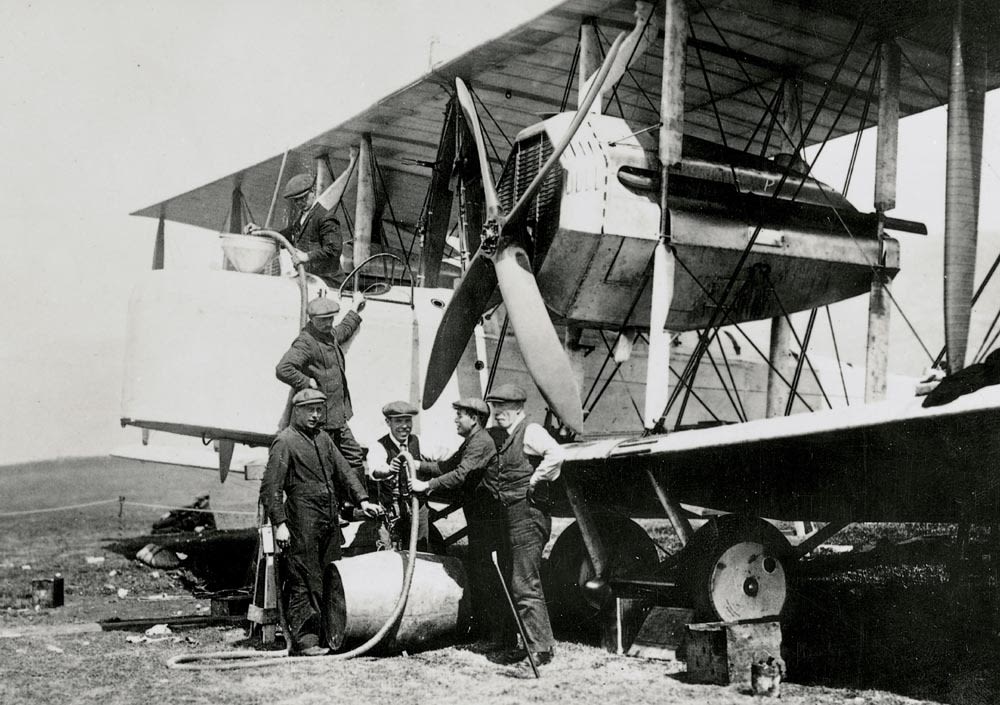
The Vickers engineering and aviation firm, which had considered entering its Vickers Vimy IV twin-engine bomber in the competition, appointed Alcock as the team’s pilot along with Brown who was adept at long-distance navigation.

In preparation for the transatlantic flight, The Vimy, powered by two Rolls-Royce Eagle 360 hp engines, was successfully converted, including replacing its bomb racks with extra petrol tanks.
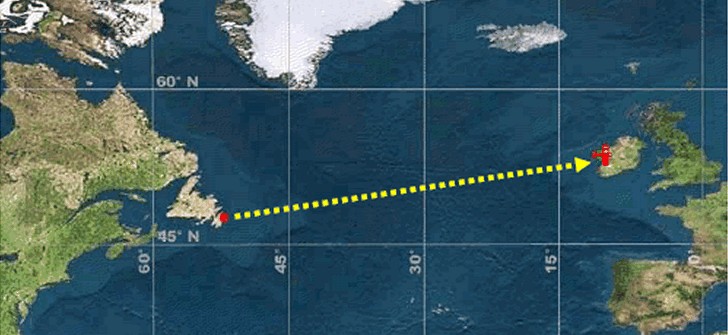
The pair took off from St. John’s, Newfoundland, in their modified bomber around 1:45pm on 14th June 1919. To say it wasn’t an easy flight would be an understatement. They encountered both mechanical and natural challenges. The wind-powered generator failed, depriving them of radio contact and much needed heating in their open-top cockpit. Fog and a snowstorm prevented navigation, almost resulting in a crash-landing at sea, not to mention the snow and freezing conditions meant the engines were in danger of icing up.
Whilst they were set a 72-hour target by The Daily Mail, the duo made landfall in Clifden, County Galway, in Ireland at 8:40am on 15th June 1919 – after just 16 hours of flight!
Incredibly, they landed not far from their intended landing zone in Ireland. However, the aircraft was damaged upon arrival because what looked like a field from their aerial view turned out to be a bog, causing the aircraft to nose-over. Thankfully neither were hurt, and Brown claimed that if the weather had been good, they’d have been able to continue to London.
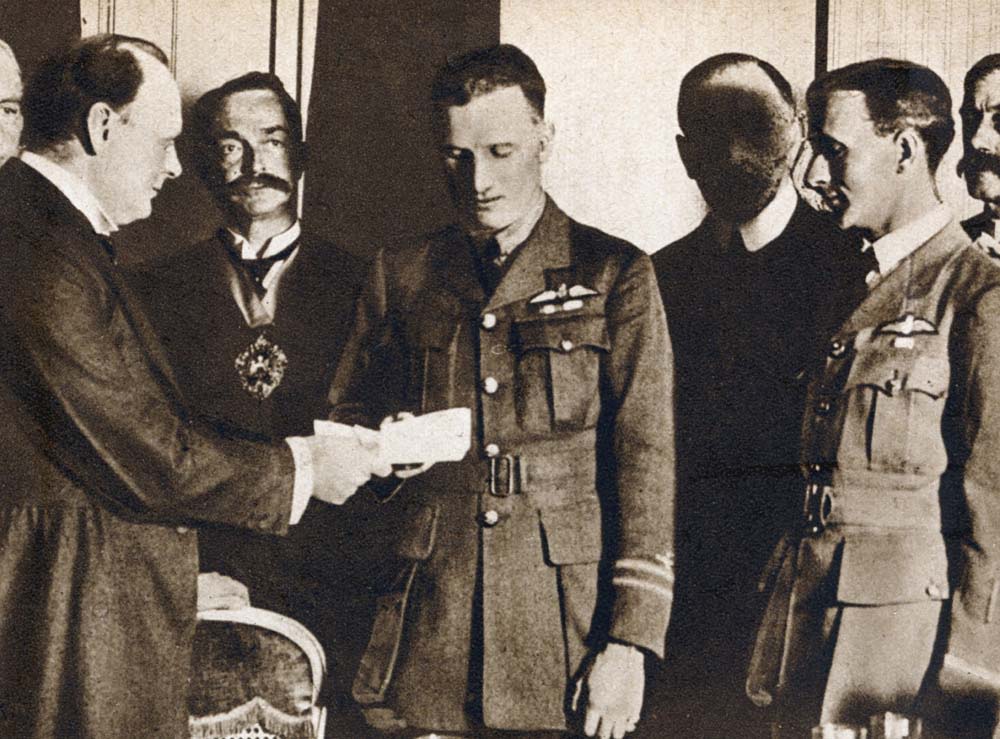
A hero’s return to a £10,000 reward
Alcock and Brown’s successful attempt meant that the fourth team, Handley Page Limited, who were yet to take-off, were no longer eligible to compete. The two airmen returned home as aviation heroes and pioneers of the sky.
As promised, Alcock and Brown were rewarded for their ground-breaking achievement – the £10,000 prize money offered by The Daily Mail, for the first crossing of the Atlantic in less than 72 consecutive hours.
The Secretary of State for Air at the time, Winston Churchill, presented the pair with their cash reward. Then one week later, at Windsor Castle, they were awarded the honour of Knight Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire by King George V.
If you’re interested…
The Royal Canadian Mint marked the milestone 100th anniversary of this remarkable achievement and feat of engineering with a limited edition 1oz Silver Proof coin. The coin features a faithful colour reproduction of the commemorative stamp that was issued to mark the 50th anniversary.
Unsurprisingly the coin proved so popular that it is no longer available at the Mint! We have a limited number remaining, click here for more information >>














